
Introduction: Reliable and Robust AI
Introduction: Reliable and Robust AI
The field of Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly evolving. It is tapping into industries and it exhibits promising transformative impacts across various sectors such as healthcare, education, finance, entertainment, and security.
AI is no longer a niche technology that only applies to the Tech sector. It has proven its value in various industries that leverage its capabilities, such as automation, analysis, speech recognition and computer vision.
However, to fully unlock its potential, AI systems must be reliable and robust. Reliable and Robust AI are AI systems that are capable of providing consistent and accurate performance under diverse conditions, taking care of unforeseen challenges and technical adversaries.
Reliability and robustness in AI are crucial for ensuring safety, trustworthiness, and fairness. Hence, if an enterprise is planning to integrate AI into its operations, then the reliability and robustness of AI applications are necessary to foster public acceptance and advance AI technologies.
- Explainability and Verification: AI systems should be built in such a way that it is transparent and explainable to the developers and users. This allows them to understand how the model works, how its logic and reasoning capability work, and what caveats one should be aware of before using the AI system.
- Model Robustness: Reliable AI employs techniques like data augmentation, distributionally robust optimization, and fine-tuning from pre-trained models to enhance the robustness of deep learning models. This ensures that the AI system is not only reliable but also robust.
- Failure Identification and Validation: AI systems may have errors and failures that affect their performance. Therefore, developers should use methods such as importance sampling, randomised smoothing, and neural network verification to estimate the probability of failure and validate the machine learning models. These methods help to reduce the errors in the AI models and improve their reliability in an enterprise setting.
- Uncertainty Quantification: Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is a key component of AI systems. UQ aims to measure and communicate the confidence and robustness of AI models. UQ can help identify sources of uncertainty, such as data noise, model misspecification, or adversarial attacks, and mitigate their impact on the performance and safety of AI systems.
Challenges and Risks in Reliable and Robust AI
One of the main goals of reliable and robust AI is to create systems that can perform complex AI tasks across different domains and environments, while still being reliable and robust to uncertainties and errors.
AI offers automation, smart analysis and various visual applications such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) and computer vision.
However, achieving such AI goals in an enterprise is not trivial. Despite a wide range of potentials and applications of AI, challenges and risks emerge when developing and deploying AI systems that lack reliability or robustness.
Below are some of the challenges and risks associated with creating reliable and robust AI:
- Safety: AI systems must not cause harm to humans, animals, or the environment, intentionally or unintentionally. The safety aspect of AI is crucial for enterprises of tomorrow that plan to integrate AI responsibly. For instance, self-driving cars must avoid collisions, medical diagnosis systems should not misdiagnose, and military robots should not harm civilians or allies. To combat this, AI models should incorporate efficient architecture, with a failure mechanism installed in case of unforeseen circumstances.
- Fairness: Bais is an inherent risk that AI carries. AI systems must not discriminate or favour certain groups or individuals based on factors like race, gender, age, or religion. The presence of bias and misinformation likewise can affect the enterprise negatively. Biassed hiring systems, discriminatory credit scoring, or censorship on social media platforms are examples of such risks. This, if overlooked, can stain the consumer and provider relationship - thereby affecting the brand image.
- Accountability: AI systems should be designed in such a way as to explain their actions and decisions. It should be equipped with mechanisms and filters that can be used by AI systems to be held responsible for their outcomes. We can see this in the form of a recommender system that justifies its suggestions, or a facial recognition system reporting its accuracy. In AI, just like any other impactful technology, accountability is essential.
- Transparency: AI systems must be understandable and interpretable by humans, both in terms of their design and behaviour. This not only allows developers to fine-tune the model and run assessment tests but also account for errors better while training the AI model. Optimised Transparent machine learning models, interpretable natural language processing systems, and explainable computer vision models are all examples of AI that contribute to transparency.
Solutions and Procedures for Reliable and Robust AI
We addressed the common challenges while developing an AI model in the previous section. We also went through how a developer could tackle those challenges.
However, every enterprise has different scale, economies and complexities in terms of its system architecture.
Thus, to ensure consistent reliability and robustness in AI, various standard methods and best practices have been proposed as follows:
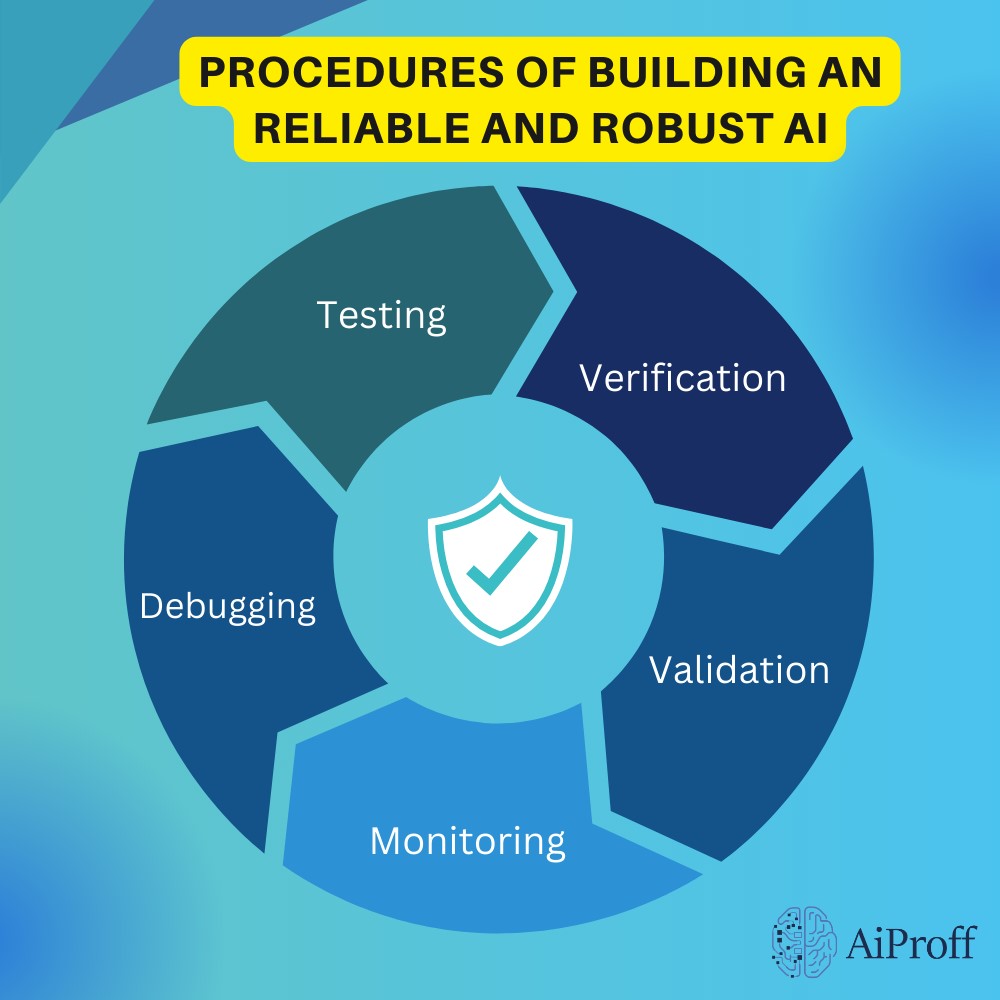
- Testing: AI systems undergo testing to check functionality and performance against predefined criteria. This standard procedure majorly includes unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing, conducted in different environments.
- Verification: Verification is built on top of testing. It is used to prove that an AI system meets formal specifications and demands. This is done by verifying how closely the AI system relies on formal methods, model checking, theorem proving, or static analysis.
- Validation: after testing and certification comes validation. Validation demonstrates that an AI system meets its intended purpose and user needs, typically through empirical evaluation, RLHF, user review, testing, or external studies and research.
- Monitoring: Monitoring observes and measures AI system behaviour over time, and accesses the performance during operation and deployment, helping detect and diagnose anomalies, errors, or deviations.
- Debugging: Debugging is the process that includes identifying and fixing problems or defects in AI systems, and enhancing code and data quality.
AI and promising future with AIProff

AI is a promising piece of innovation, but it has its caveats. For enterprises of today and the future, it is important to embrace this new technology with caution.
As you can see from the previous sections, a lot of focus was made on designing a reliable and robust AI design. Poor planning of AI systems can lead to many issues - reliable AI won’t always be reliable, and robust AI won't always be robust.
Every enterprise has its own needs and scale, which makes it difficult to create a consistent AI application.
Thus, it all comes down to human expertise who design, develop and implement these AI systems that align with the needs of the enterprise. As demand for AI solutions grows, the need for reliable and robust AI platforms to support enterprise-scale development and deployment becomes paramount.
Here's where AiProff comes to your service.
AIProff is a leading provider and developer of AI/ML-based applications that empower enterprises to create, manage, and optimise AI applications with confidence and ease.
AIProff's expertise and services span the entire AI lifecycle, from data ingestion and preparation to model building and training, and ultimately deployment and monitoring.
We offer solutions in:
- Automated Testing: Verify functionality, performance, and accuracy of AI models.
- Explainable AI: Generate human-readable explanations for AI model decisions, enhancing transparency.
- Adversarial Robustness: Protect AI models from malicious attacks, ensuring security and integrity.
- Fairness and Bias Detection: Measure and mitigate potential biases and unfairness in AI model outcomes, promoting fairness and ethics.
and many more
In the evolving landscape of AI, AIProff is here to help you achieve your AI goals and overcome challenges, ultimately creating reliable and robust AI systems for the benefit of enterprises and society.
If you're interested in learning more about how AiProff can support your AI initiatives, visit our website or reach out to us today.
We welcome new partners and collaborators who share our vision of a more reliable and robust AI future.
Introduction: Reliable and Robust AI
Related Articles

Sept 22, 2023
Introduction: When AI starts to predict Future
Forecasting is the art and science of predicting future events or outcomes based on past and present data.

Sept 22, 2023
Introduction to NLP: When AI talks
The field of Artificial intelligence is exciting. Under this discipline of Technology,

Sept 22, 2023
Introduction to Computer Vision: When Machines Start to See
The quest for intelligence has been going on for ages, and the question of